ForInter
BAVARIAN RESEARCH ASSOCIATION INTERACTION OF HUMAN BRAIN CELLS

Role of autophagy-associated processes in the pathophysiology of PD
Field of work:
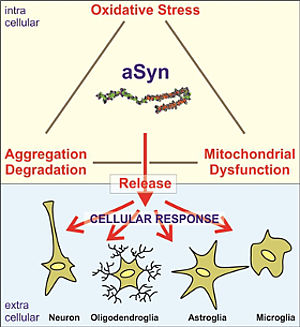
Investigation of biological alterations and functional deficits in neural and glial cellsAutophagy describes the controlled intracellular degradation of dysfunctional proteins and cellular structures. Impaired autophagy of the alpha synuclein protein and of mitochondria – the main site of energy production in neurons – results in dysfunction and death of dopaminergic neurons and is considered a central pathological process in genetic forms of Parkinson’s disease. It is currently unknown, if and how impaired autophagy contributes to the development of sporadic forms of Parkinson’s disease. To fill this gap, we will study autophagy and autophagy related processes in neurons generated from patient derived induced pluripotent stem cells using state of the art methods in biochemistry, molecular biology, and imaging. In addition we will investigate the impact of stressors on neuronal health and autophagy to determine the influence of environmental factors on disease development. Collectively, these studies are expected to provide important novel insight into the role of autophagy in the development of sporadic forms of Parkinson’s disease.
Project partners:
- Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg
- Technische Universtität München (TUM)



